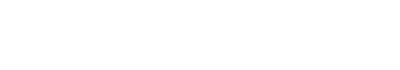As we continue to move into the digital age, security has become one of the greatest concerns of our technologically integrated lives. A vast percentage of people in any first-world country own a smartphone, use a computer, or have access to the internet. We store our pictures, memories, personal information, and our lives on our devices.
And what do we use to protect ourselves? A password. Maybe it is a four-digit code or a more complex array of connected dots, either way, passwords are what stands between our privacy and exposure in our digitized world.
This reach of connectedness has also made its way into the hands of today’s workforce. With more and more handheld devices being used in day-to-day operations, a greater burden of security has been placed upon companies to keep their data secure. Strong passwords are a start to protect information, but additional authentication methods can improve security and also improve efficiency.
We have seen many features of consumer devices make their way to rugged devices, and the latest hardware security feature to make that jump is biometric readers. Manufacturers have added front-facing cameras and fingerprint readers to their newest models and will continue to invest in those areas.
In a professional setting, shared networks, devices, and computers not only host sensitive company information but the bank accounts, addresses, and other personal data of their employees.
Biometric Authentication may be the best line of defense standing between your organization’s most important data and a potential cyber attack.
Boost workforce security with biometric authentication – Get in touch with Bluefletch!
Benefits of Biometric Authentication
Enhanced Security: Biometric authentication provides a higher level of security compared to traditional methods like passwords or PINs. Biometric features, such as fingerprints, iris patterns, or facial characteristics, are unique to each individual, making it difficult for unauthorized access.
Convenience and User Experience: Biometric authentication eliminates the need to remember complex passwords or carry physical tokens. Users can simply use their own biometric traits for seamless and quick authentication, improving the overall user experience.
Strong Identity Verification: Biometric authentication offers reliable identity verification. It ensures that individuals accessing sensitive systems or data are indeed who they claim to be, reducing the risk of identity theft or impersonation.
Non-Transferable: Unlike passwords or access cards, biometric traits cannot be easily replicated, stolen, or shared. This makes it more difficult for malicious actors to gain unauthorized access by impersonating someone else.
Reduced Fraud: Biometric authentication significantly lowers the risk of fraud since it is difficult to forge or replicate biometric features. This is especially important in sectors such as banking, healthcare, and government where preventing fraud is critical.
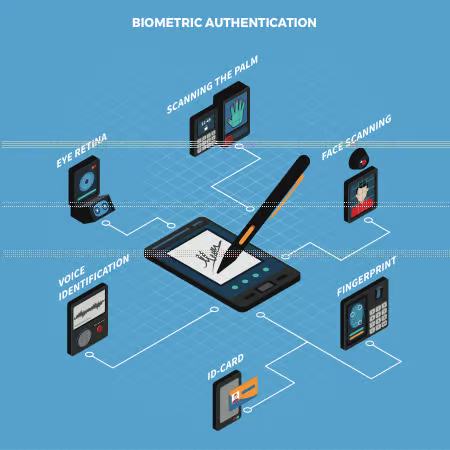
What is Biometric Login?
Biometric Authentication is a form of data security that identifies individuals based on their unique biological characteristics such as fingerprints, faces, voices, or other biometric identifiers.
Authenticators can be used to grant access to buildings, computer systems, databases, secure networks, devices, and so much more.
For shared device environments, biometric authentication can greatly increase the security an enterprise needs to maintain a secure digital workspace. By limiting access to company systems via employees’ physical attributes, there is an extra sense of comfort in the workplace. Now, security goes beyond just something you know (password) and includes who you are (biometrics).
The strength of biometric authentication lies in the unique nature of its requirements; utilizing biological information makes for a far more secure user experience than a traditional password that can easily be shared.
However this is in no way a perfect system, and biometric authentication methods have the potential to be hacked no differently than other password or security systems. It is important to stay informed about the latest technologies and biometric information to keep your enterprise secure.
In this article, we will be detailing how biometric authentication can work for you in the workplace, where it thrives, how it works, and why you should make the switch to a more secure and also efficient user experience.
Considerations for Biometric Authentication
Privacy Concerns: Collecting and storing biometric data raises privacy concerns.Organizations must ensure proper data protection measures are in place to safeguard sensitive information. Compliance with relevant data protection regulations, such as GDPR, is crucial.
Cost and Complexity: Implementing biometric authentication requires investment in specialized hardware, software, and infrastructure. It may also involve integration with existing systems, which could be complex and time-consuming.
Failure Rates: Biometric systems may encounter false acceptance or false rejection errors. Factors like environmental conditions, injury, or aging can impact the accuracy of biometric readings. Proper system calibration and monitoring are essential to minimize such errors.
Scalability and Compatibility: Biometric authentication systems should be designed to scale efficiently as the number of users increases. Additionally, compatibility with existing IT infrastructure and applications may need to be considered during implementation.
User Acceptance: Some users may feel uncomfortable sharing their biometric data due to privacy concerns or cultural reasons. Organizations must communicate the benefits and security measures effectively to gain user acceptance and address any concerns.
How does it Authenticate End-Users?
Biometric Authentication works similarly to a password, except that the end-user’s unique physical attributes are their password. Where digits and numerals would be used for authentication, a biometric authenticator uses the pattern or image of a physical trait such as your fingerprint or face to grant entry to shared systems, company databases, and physical buildings.
Everyone who needs access to a particular database or device is limited to their biological characteristics. A system will only give permission to a user who matches the biological information, such as a fingerprint, that is on file.
For example, if an organization was using a fingerprint scanner to authenticate users, their biometric technology would most likely read the lines and grooves of a fingerprint to make a digital hash for storage. This is opposed to an exact picture or a replica of someone’s finger because of certain privacy laws that are set in place to protect individual privacy.
The EU has a very strict regulation known as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) which protects individual data by regulating how information is stored and used. Their official site states, “data includes genetic, biometric, and health data, as well as personal data revealing racial and ethnic origin, political opinions, religious or ideological convictions or trade union membership.”
Therefore, most systems wishing to utilize biometric authentication typically leverage the digital mapping strategy instead of true copies to protect a user’s identity from hackers. The mapped value of the fingerprint is then stored securely into the device’s system where it can not be accessed.
Naturally, the copy needs to be secured properly since a compromised fingerprint could threaten the personal safety and future security of a user. When a person places their finger on a scanner the system will trace out the lines of their fingerprint and match it to the digital map on file, eventually granting access once the fingerprint is recognized.
Matches do not have to be 100% accurate per the personal privacy regulations and the technology’s advanced understanding that biological attributes may become scarred or affected by natural causes.
This is an ideal scenario for enterprises that have workspaces with shared devices because authentication time is much quicker than entering a traditional password.
In a workplace utilizing biometric authentication, every person already has their own password, making this form of authentication one of the most secure options for any enterprise that uses shared technology.\
Enhance efficiency through biometric solutions – Request a demo today!
What are the Different Types of Authentication?
There are many different forms of biometric authentication that can help organizations with a variety of security wants and needs.
- Fingerprint Authentication
-
-
- One of the most common forms of biometric authentication. Uses a person’s fingerprint to create a digital mapped value that can later be used to authenticate a user into a shared system or location.
-
- Facial Recognition
-
-
- An emerging technology that is continuing to gain more traction in the mobile world with companies like Apple and Android beginning to integrate forms of facial recognition into their company-owned devices.
- Much like fingerprint authentication, facial recognition uses a mapped value of an individual’s facial features to create a unique passcode within a system.
- Facial recognition requires special hardware such as a high-resolution front-facing camera that can detect and match facial features to the stored mapped value. Learn more about Facial Recognition here!
-
- Voice Identification
-
-
- Less common in consumer and enterprise use, voice ID uses the waveforms of a person’s voice to confirm their identity.
- This technology has begun to appear in the consumer market with devices like Amazon’s Alexa which has the capability to recognize and remember individual voices by tracing and storing vocal patterns.
-
- Retina Scanning
-
- On the horizon is retina scanning, but the hardware is still a few years away from reaching the enterprise market.
A Step-By-Step Process For Implementing Biometric Authentication
Step 1: Identify the Needs and Objectives Before implementing biometric authentication, clearly define the objectives and identify the specific needs of your business. Consider factors such as security requirements, user convenience, compliance regulations, and the systems or applications that require authentication.
Step 2: Conduct a Feasibility Study Evaluate the feasibility of implementing biometric authentication in your organization. Assess the existing IT infrastructure, hardware, and software compatibility. Consider the costs involved, including procurement of biometric devices, software licenses, and any necessary system modifications.
Step 3: Choose the Appropriate Biometric Modality Select the most suitable biometric modality based on your specific requirements. Common options include fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, iris scanning, voice recognition, or a combination of multiple modalities. Consider factors such as accuracy, ease of use, scalability, and user acceptance.
Step 4: Define Security Policies and Procedures Develop comprehensive security policies and procedures that govern the use of biometric authentication within your organization. Clearly outline guidelines for data storage, access controls, user privacy, data retention, and compliance with relevant regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
Step 5: Select a Reliable Biometric Authentication System Choose a reliable biometric authentication system from a reputable vendor. Evaluate factors such as system accuracy, scalability, compatibility with existing infrastructure, integration capabilities, and vendor support. Consider conducting pilot tests or requesting demos to ensure the chosen system meets your requirements.
Step 6: Develop Data Protection Measures Implement robust data protection measures to safeguard biometric data. Ensure encryption during storage and transmission, strict access controls, regular backups, and an incident response plan for potential breaches. Comply with applicable data protection regulations to maintain user trust.
Step 7: Integrate with Existing Systems Integrate the biometric authentication system with existing IT systems and applications. Coordinate with relevant teams, such as network administrators, software developers, and system integrators, to ensure seamless integration without disrupting regular operations.
Step 8: Conduct User Training and Communication Organize training sessions to educate users about the biometric authentication system. Provide clear instructions on how to enroll and use their biometric data for authentication. Address any concerns or misconceptions about privacy and security to gain user acceptance and cooperation.
Step 9: Test and Evaluate Thoroughly test the biometric authentication system in different scenarios to ensure accuracy and reliability. Conduct pilot tests with a limited group of users before deploying it organization-wide. Gather feedback, track performance metrics, and make necessary adjustments to optimize the system.
Step 10: Deployment and Ongoing Maintenance Once thoroughly tested, deploy the biometric authentication system across the organization. Monitor system performance, conduct regular maintenance, and keep up with software updates and security patches. Provide ongoing technical support for users and promptly address any issues that arise.
By following these steps, IT specialists can successfully implement biometric authentication within their business, enhancing security and user experience while adhering to privacy regulations.
Reach Out Today for a 30 Day Demo! Try Bluefletch page
Where is it Used?
In 2013 Apple released their iPhone 5s which featured the first-ever fingerprint scanner on an iOS home button. It was used to authenticate users and unlock the device as a faster and more secure alternative to their standard numerical passcode. While fingerprint scanning was not a new invention in 2013, it was one of the first times that the consumer market would get a hold of this technology, and it has become a staple across almost every smartphone ever since.
Among the many use cases for biometric authentications, the fingerprint ID scanner on modern-day smartphones is the most common and well-known form. Essentially all major players in the mobile device market have some form of biometric login at work. It is second nature for most smartphone users to log in to their devices and applications with their fingerprints.
With smartphones being in the hands of a majority of today’s workforce, having shared devices with biometric authentication would be a natural transition from a password for many users.
Biometric login alleviates the need for users to remember complex passwords, or worry about their data knowing that only their unique biological traits can be used to access their information. This is an ideal solution for enterprises that command a fleet of shared Android devices that have to be accessed by multiple employees.
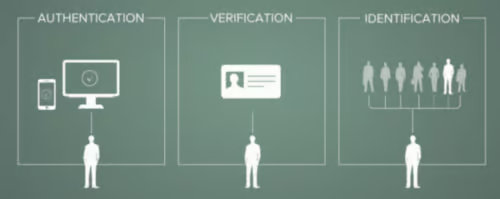
Options for Shared Device Environments
Android is the leader in mobile enterprise technology, providing the most customizable and streamlined user experience for the retail workforce with their range of rugged devices. Android has a plethora of devices fitted with a fingerprint scanner, which makes for a more secure user experience in the work environment.
Due to the vast number of Android and smartphone users being acclimated to using fingerprint scanners, biometric login will feel comfortable and familiar in the workplace.
Unlocking a shared Android device with a fingerprint means a quicker login time and better employee performance. It gives employees the confidence to perform highly on a daily basis without the anxiety of forgetting or having to reset their password on the job.
This allows an organization’s Helpdesk team to focus on maintaining the security of daily operations knowing that employees no longer have to flood the call center will annoying password reset requests. In turn, this clears up the ticket queue and boosts overall business productivity.
In addition to providing a secure login experience, biometric authentication can also be used for point of sale operations. Android devices allow users to make purchases from the Google Play store with their fingerprint scanners. This can be translated to the retail environment as devices can be used to make sales on the floor with tools like Oracle Xstore which require biometric authentication
Our BlueFletch Enterprise Launcher is built to perform on the rugged Android devices that employees rely on. Enterprise Launcher comes integrated with the latest biometric login software to create digital maps and securely store biometric data on enterprise devices so your company doesn’t have to worry about potential data leaks.
The Enterprise Launcher works alongside existing Android biometric authentication technology to provide a safer end-user experience.
Secure your workforce with cutting-edge biometrics – Consult Bluefletch experts now!
Passwords vs. Biometrics
Passwords have long been the standard security measure for every electronic device, shared system, or digital database. However, with the increased dependence on technology and the rise in cybercrime, passwords have become weaker and less sustainable.
Biometric authentication alleviates the need for users to remember complex passwords, or worry about their data knowing that only their unique biological traits can be used to access their information.
Passwords are vulnerable to being leaked, and unfortunately, many users never learn how to make the most secure passwords, leaving their information exposed. This attribute carries over to the corporate world where employees find their passwords being leaked despite trying to follow their company’s password regulations. If your enterprise does not have a strong enough IT team to implement password security, your information could be at risk.

Biometric login can combat some of the weaknesses of passwords by providing a better login experience. Fingerprints can not be written down or stolen in the same way that a password can, but that does not mean hackers can’t access the digitized versions.
Despite being more secure than a traditional password, biometric information is not 100% safe as savvy hackers can still find a way to steal fingerprint patterns and other identifiers that are not properly secured. It is crucial that organizations utilize the proper software and technology to store biometric information.
Unlike passwords, the biometric hash is stored in a device, not a cloud. A user’s fingerprint or facial pattern should be locked into each device they need access to, not a network or cloud system. If stored in a compromised position hackers can easily access the digital maps and gain entry to workplace systems.
How to Keep Biometric Information Secure
Implementing biometric authentication brings enhanced security to your organization, but it also introduces the need to protect sensitive biometric data. Here are some essential measures to keep biometric information secure:
Encryption: Ensure that all biometric data, both at rest and in transit, is encrypted using robust encryption algorithms. This prevents unauthorized access to the data even if it is intercepted or compromised.
Secure Storage: Store biometric data in secure systems, such as encrypted databases or secure servers, with restricted access controls. Implement proper user access management and role-based permissions to limit access to authorized personnel only.
Anonymization and Pseudonymization: Consider anonymizing or pseudonymizing biometric data whenever possible. This involves removing personally identifiable information or replacing it with a unique identifier, reducing the risk of breach or misuse.
Secure Data Transmission: When transmitting biometric data over networks or between systems, ensure the use of secure protocols such as HTTPS or VPNs. Implement strong network security measures like firewalls and intrusion detection systems to prevent unauthorized access.
Data Minimization: Only collect and store necessary biometric data. Avoid collecting excessive or unnecessary data beyond what is required for authentication purposes. Regularly review data retention policies and delete or dispose of biometric data when it is no longer needed.
Strong Authentication Controls: Implement multi-factor authentication for system access, combining biometrics with other authentication factors (such as passwords or tokens) for added security. This provides an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access.
Regular Auditing and Monitoring: Conduct regular audits and monitoring of the biometric authentication system to detect any unusual activities or potential security breaches. Implement log management and monitoring tools to track user access, system events, and potential security incidents.
Employee Training and Awareness: Provide comprehensive training to employees who handle or have access to biometric data. Educate them about the sensitivity of biometric information and their responsibilities in maintaining its security. Reinforce the importance of following security protocols and reporting any suspicious activities promptly.
Compliance with Data Protection Regulations: Ensure compliance with relevant data protection regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, or other local privacy laws. Understand the requirements for storing, processing, and transferring biometric data, and implement necessary safeguards to meet these regulations.
Regular Software Updates and Patching: Keep the biometric authentication system and associated software up to date by applying regular software updates and patches. These updates often include security enhancements that address vulnerabilities and protect against emerging threats.
By following these best practices, IT specialists can effectively safeguard biometric information and maintain the highest level of security when implementing biometric authentication within their organization.
A Couple of Companies That We’ve Implemented Biometric Authentication For
We just need a list of companies where we’ve implemented biometric authentication, preferably our more well-known companies
Takeaways
It is the responsibility of an organization’s leaders to do everything in their power to protect and serve the employees that make their business run on a daily basis. In a lot of work environments, this empowerment comes in the form of shared devices and technology. Shared devices such as mobile rugged Androids, ruggedized iOS smartphones, and other technology keep a workplace running efficiently by allowing employees to work faster and smarter.
Making the switch to biometric authentication might be the change your enterprise needs to create a safe and secure work environment for your end-users. By keeping device and workplace systems protected.
For more information about how BlueFletch can help your enterprise adopt safer enterprise security features on your mobile devices, contact us at info@bluefletch.com