Retail consistently leads the charge in technology innovation, driven by several key factors. These include the pivotal role of mobile device ecosystems, evolving shopping demographics, and the profound influence of e-commerce giants like Amazon. Here’s a comprehensive look at how these elements contribute to the rapid advancement of technology in the retail sector.
The Impact of Mobile Device Ecosystems
A decade ago, retailers faced a new reality: customers entered stores equipped with powerful smartphones and extensive product knowledge. This shift compelled retailers to equip their store associates with similar tools to meet and exceed customer expectations. Early investments in comprehensive websites during the early 2000s empowered customers with detailed product information and availability, fundamentally altering the retail landscape.
To bridge the gap between tech-savvy customers and their associates, retailers adopted mobile devices for store employees. This move ensured that staff could provide better service and stay competitive. Initially, associates often used personal smartphones to answer customer queries, but now retailers have provided advanced devices, enhancing the in-store experience. This transformation was necessary to keep pace with the increasing capabilities of consumer technology.
Retailers invested in mobile technology to ensure that employees could access real-time data about inventory, product specifications, and customer preferences. Mobile point-of-sale (POS) systems became commonplace, allowing for quicker and more efficient checkouts. These devices also enabled store associates to process transactions anywhere within the store, significantly enhancing the customer experience.
Furthermore, mobile devices allowed employees to stay connected with other parts of the business. For instance, if a product was out of stock at one location, employees could quickly check availability at nearby stores or warehouses. This level of connectivity and real-time information sharing significantly improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
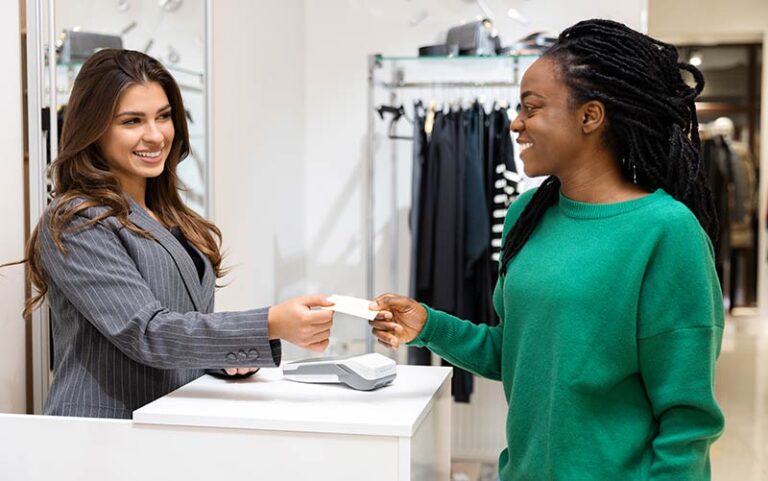

Changing Shopping Demographics
The evolving shopping demographics, particularly among younger consumers, significantly drive retail innovation. Younger shoppers seek seamless and informed shopping experiences, both online and in physical stores. They expect store associates to be subject matter experts, given the effort required to visit a store.
These high-intent shoppers, who may not remember now-defunct retailers like Circuit City or Toys R Us, have modern retail experiences that shape their expectations. For them, visiting a store is often a last resort after extensive online research. Therefore, retailers must ensure that their in-store experience is exceptional and meets the high expectations of these informed customers.
This shift in demographics has prompted retailers to rethink their strategies. Younger consumers are digital natives who value convenience, speed, and personalized experiences. They are accustomed to instant access to information and expect the same level of service in physical stores. Retailers have responded by integrating technology into every aspect of the shopping experience.
One example of this is the rise of omnichannel retailing. This approach integrates online and offline channels to provide a seamless shopping experience. Customers can browse products online, check their availability in nearby stores, and even reserve items for in-store pickup. This convergence of digital and physical retail ensures that customers have a consistent experience regardless of how they choose to shop.
Retailers are also leveraging data analytics to understand and predict consumer behavior. By analyzing data from various touchpoints, retailers can gain insights into customer preferences and tailor their offerings accordingly. This data-driven approach enables retailers to create personalized experiences that resonate with younger shoppers.
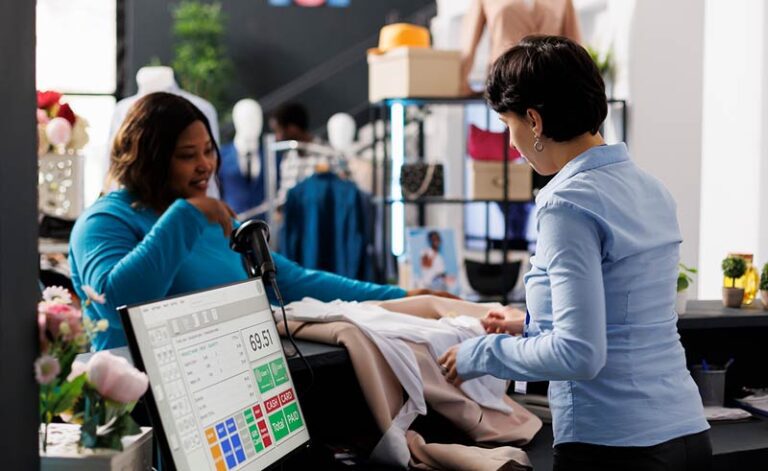

The E-commerce Revolution and Amazon’s Influence
E-commerce, particularly Amazon’s disruptive influence, has profoundly impacted the retail industry. Amazon started as an online bookstore and gradually expanded into various product categories, revolutionizing retail with innovations like Amazon Prime, free deliveries, and easy returns. This disruption forced traditional retailers to innovate or risk obsolescence.
Amazon’s ability to iterate and innovate without the constraints of physical stores allowed for rapid implementation of changes. This model of continuous improvement and learning from previous releases has become a benchmark for other retailers. Amazon’s approach has pressured other retailers to enhance their web and mobile presence and improve their overall customer experience.
Amazon’s influence extends beyond its business model. The company’s commitment to customer-centricity has set a new standard for the retail industry. Amazon Prime, with its promise of fast and free shipping, has raised consumer expectations for delivery times and convenience. Traditional retailers have had to adapt by offering similar services to remain competitive.
Additionally, Amazon’s use of data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) has transformed the way retailers operate. The company’s recommendation algorithms, for example, provide personalized product suggestions based on past purchases and browsing behavior. This level of personalization has become a key differentiator in the retail industry, prompting other retailers to invest in similar technologies.
The rise of Amazon has also led to the proliferation of smaller retail products and brands that operate exclusively online. These direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands leverage e-commerce platforms to reach a global audience without the need for physical stores. This shift has democratized retail, allowing niche brands to thrive and compete with established players.
Retailers have responded by integrating technology into every aspect of the shopping experience
The Importance of Margins and Efficiency
Margins and efficiency play crucial roles in retail. The industry operates on thin margins, especially in sectors like grocery, where every dollar of revenue translates to mere pennies of profit. This financial reality drives retailers to adopt technologies that improve efficiency and accuracy. For instance, a 10% improvement in inventory accuracy can significantly impact profit margins.
Retailers must adopt a long-term, detail-oriented approach, similar to Formula 1 racing, where every small improvement counts. A culture of experimentation and iteration is essential, continuously seeking small wins that accumulate into significant gains over time.
Improving efficiency involves optimizing various aspects of the supply chain, from procurement and logistics to inventory management and sales. Retailers are increasingly using technology to streamline these processes. For example, radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags help track inventory in real-time, reducing the risk of stockouts and overstocking. Automation and robotics in warehouses improve order fulfillment speed and accuracy, further enhancing operational efficiency.
Also, retailers are leveraging predictive analytics to forecast demand and plan inventory accordingly. By analyzing historical sales data and considering factors like seasonality and market trends, retailers can make more informed decisions about stock levels. This proactive approach minimizes waste, reduces costs, and ensures that popular products are always available to meet customer demand.
Rapid Feedback Loops and Proof of Concepts
One unique advantage of the retail industry is the rapid feedback loop from customers. Hyper-local deals and micro-targeted promotions allow retailers to quickly gauge the effectiveness of their strategies. This fast feedback mechanism enables retailers to adjust their approaches in real time, optimizing marketing and sales efforts.
Running proof of concepts (POCs) efficiently is crucial. Retailers can test new ideas quickly and measure their impact using existing technologies like point-of-sale (POS) systems and security cameras. By analyzing these data points, retailers can make informed decisions about which innovations to pursue further.
The rapid feedback loop in retail allows for agile decision-making. Retailers can launch new initiatives, gather customer feedback, and make adjustments within a short period. This iterative process ensures that retailers remain responsive to changing market conditions and customer preferences.
For instance, retailers can experiment with different store layouts, product placements, and promotional strategies to see what resonates with customers. By monitoring sales data and customer behavior, retailers can identify successful tactics and scale them across their stores. Conversely, if an initiative does not yield the desired results, retailers can quickly pivot and try a different approach.
Technology plays a vital role in enabling these rapid feedback loops. Advanced analytics platforms provide real-time insights into customer interactions, sales performance, and inventory levels. Retailers can use these insights to optimize their operations and make data-driven decisions that enhance the customer experience.
The Role of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality (AR), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are further driving innovation in retail. These technologies are reshaping the way retailers interact with customers and manage their operations.
AI is being used to enhance various aspects of the retail experience. Chatbots and virtual assistants provide instant customer support, helping shoppers find products, answer questions, and complete purchases. AI-powered recommendation engines analyze customer behavior to deliver personalized product suggestions, increasing the likelihood of conversion.
Augmented reality (AR) is transforming the way customers shop for products, particularly in categories like fashion and home decor. AR applications allow customers to visualize how products will look in their homes or on their bodies before making a purchase. This immersive experience reduces uncertainty and enhances customer confidence in their buying decisions.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing inventory management and supply chain operations. IoT-enabled sensors and devices provide real-time data on product movement, storage conditions, and equipment performance. This connectivity allows retailers to monitor their supply chain end-to-end, ensuring optimal efficiency and reducing the risk of disruptions.
Summary
Several key reasons drive retail’s leadership in technology innovation:
- Customer and Employee Experience:
Empowering employees with the right tools to meet customer expectations and enhance the overall shopping experience. - Margin and Efficiency:
Leveraging technology to improve efficiency and accuracy, thus enhancing profit margins and operational performance. - Rapid Feedback and Innovation:
Utilizing fast feedback loops and proof of concepts to innovate and adapt quickly, ensuring responsiveness to market changes and customer needs.
Retailers’ ability to experiment, measure results, and iterate rapidly sets them apart from other industries. As technology and customer expectations continue to evolve, the retail sector’s commitment to innovation will remain crucial for its success. Emerging technologies like AI, AR, and IoT will further drive this innovation, enabling retailers to deliver exceptional experiences and maintain their competitive edge. Get started today!